What Are Punch Dies?
Punch Dies, also known as punching tools or stamping dies, are precision tools used in manufacturing to cut, shape, or form materials (typically metals) into specific shapes through mechanical force. These tools consist of two primary components: the punch (upper component that applies force) and the die (lower component that contains the desired shape). Punch Dies operate with tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm for high-precision applications and can withstand forces up to 2,500 tons in heavy industrial presses.
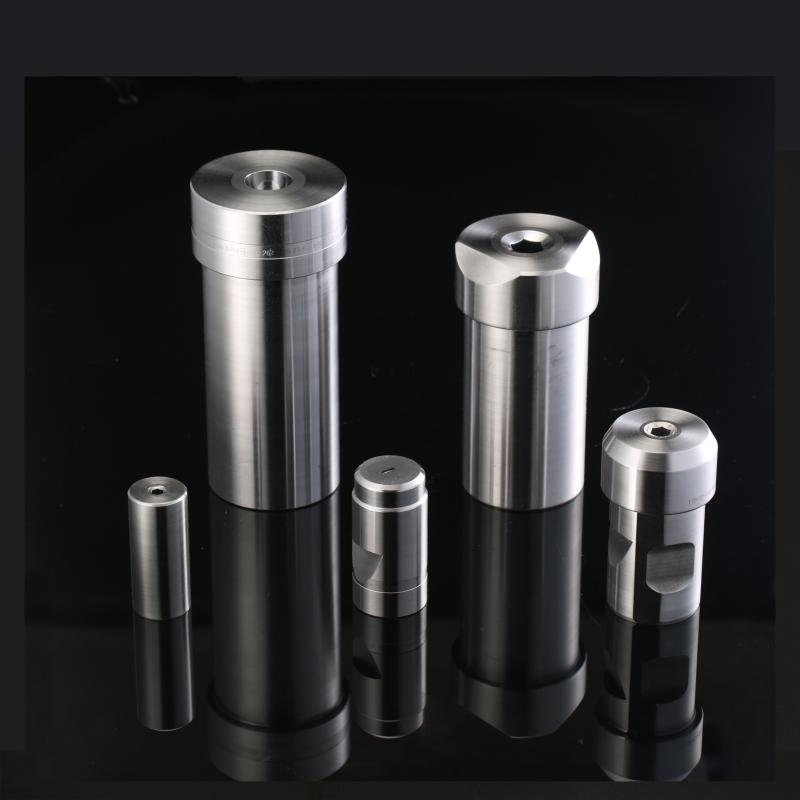

Key characteristics of modern punch dies include:
Material Composition: Typically made from tool steels like D2 (HRC 58-62) or Tungsten Carbide for extended service life (often exceeding 1 million cycles)
Surface Treatment: Often coated with TiN (Titanium Nitride) or TiCN (Titanium Carbo-Nitride) to enhance wear resistance, increasing lifespan by 300-400%
Precision: Capable of maintaining dimensional accuracy within 0.01-0.05 mm depending on application requirements
Speed Capability: High-speed dies can operate at 1,200 strokes per minute in progressive die applications
Temperature Resistance: Specialized dies can withstand operating temperatures up to 500°C for hot stamping applications
Applications of Punch Dies
Punch dies serve critical functions across multiple industries due to their versatility and precision:
1. Automotive Industry
In automotive manufacturing, punch dies produce body panels, chassis components, and interior parts with thicknesses ranging from 0.5 mm to 6 mm. Progressive dies can create complex brackets with 20+ operations in a single tool, achieving production rates of 600-800 parts per hour.
2. Electronics Manufacturing
Precision micro-dies create connectors and shielding components with feature sizes as small as 0.1 mm. Fine blanking dies achieve edge quality with 90-95% shear surface, critical for electrical contacts.
3. Aerospace Components
Titanium and Inconel parts are formed using heated dies (300-450°C) to reduce springback. Aerospace dies maintain positional accuracy within ±0.025 mm across large components.
4. Appliance Manufacturing
High-volume production of stainless steel sinks and oven panels utilizes compound dies that combine 4-6 operations simultaneously, processing material up to 3 mm thick.
5. Medical Device Production
Surgical instrument components are stamped using micro-precision dies with surface finishes of Ra 0.2 μm or better to prevent bacterial adhesion.
Maintenance Procedures for Punch Dies
Proper maintenance extends die life and ensures consistent part quality. Follow this comprehensive maintenance protocol:
Daily Maintenance
Inspect cutting edges for chipping or wear using 10x magnification
Clean die surfaces with non-abrasive solvents (flash point > 60°C)
Verify proper lubrication (applying 2-5 μm film thickness)
Check guide post clearance (<0.01 mm runout)
Weekly Maintenance
Measure punch and die clearance using feeler gauges (typically 5-10% of material thickness)
Inspect spring pressures (±10% of specified value)
Verify stripper plate parallelism (<0.02 mm/m)
Check nitrogen cylinders in gas springs for proper pressure (50-150 bar)
Monthly Maintenance
Disassemble and polish components with 600-1200 grit stones
Inspect for micro-cracks using dye penetrant testing
Measure critical dimensions with CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine)
Recondition cutting edges when wear exceeds 0.05 mm
Advanced Maintenance Techniques
For maximum die performance:
Implement laser cladding to rebuild worn surfaces with 0.1 mm precision
Use EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) for sharpening complex profiles
Apply PVD coatings when original coating wear exceeds 30%
Perform dynamic analysis with strain gauges during operation
Storage and Handling Best Practices
Proper storage prevents corrosion and maintains dimensional stability:
Store in climate-controlled environments (20±2°C, 40-50% RH)
Apply vapor corrosion inhibitor (VCI) with 0.5-1.0 g/m³ concentration
Use dedicated racks with 10-15 cm clearance between dies
For long-term storage, purge containers with nitrogen (<1% O₂)
Optimizing Punch Die Performance
To achieve peak efficiency in punch die operations:
Match punch/die clearance precisely to material type and thickness (e.g., 8% for mild steel, 6% for stainless)
Maintain press parallelism within 0.03 mm/m
Optimize stripper timing (0.5-1.0 mm before punch contact)
Monitor punch penetration (0.5-1.5 mm into die for clean shearing)