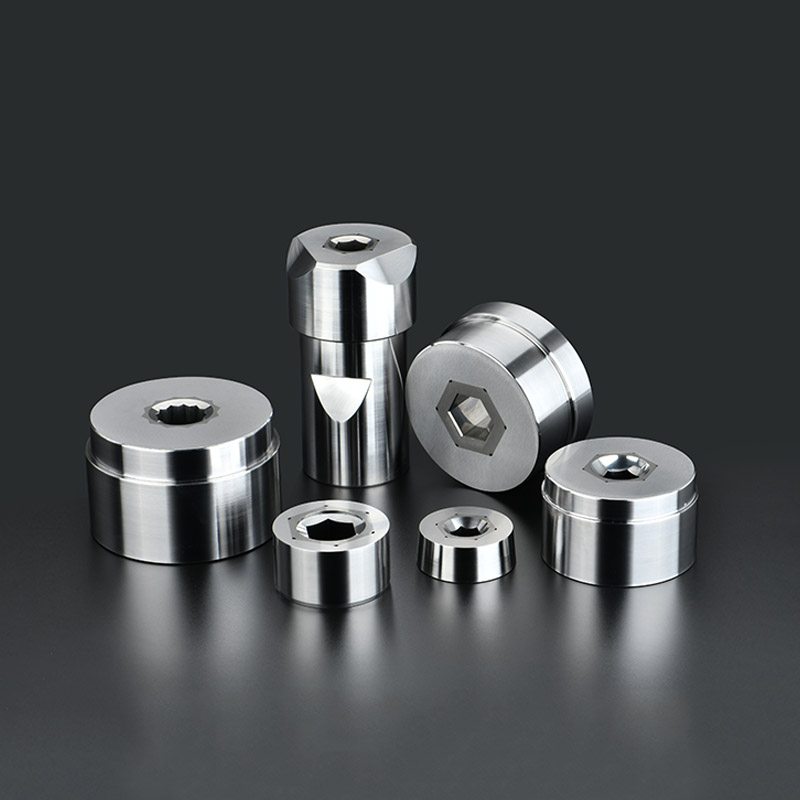
In modern fastener manufacturing, precision, efficiency, and durability are crucial. Cold Heading Molds are the backbone of the cold forming process, enabling manufacturers to produce bolts, screws, rivets, and other metal fasteners with exact dimensions and superior mechanical properties.

What Is a Cold Heading Mold?
A Cold Heading Mold is a specialized tool used in cold forming processes, where metal wire or rod is shaped into fasteners without melting. Unlike machining or hot forging, cold heading uses high pressure to plastically deform the metal at room temperature. The mold determines the final shape, size, and features of the fastener, making it an essential component in high-volume production.
How Does a Cold Heading Mold Work?
Wire Feeding: Metal wire or rod is fed into the mold.
Die Closure: The mold closes, holding the material in position.
Cold Heading Action: A punch presses the wire into the die cavity, forming the head and shank.
Ejection: The newly formed part is ejected, ready for secondary operations such as threading or heat treatment.
This process ensures minimal material waste, excellent surface finish, and high dimensional accuracy.
Types of Cold Heading Molds
Cold heading molds are classified based on head type and function:
Hex Head Molds: For bolts and screws with hexagonal heads.
Round Head Molds: For rivets and fasteners with smooth round heads.
Countersunk Head Molds: For flat-head screws and precision fasteners.
Custom Molds: Designed for specialized fasteners according to client specifications.
Additionally, molds can vary by material (high-speed steel, alloy steel, or carbide) and by stage (single-step or multi-step forming).
Applications of Cold Heading Molds
Cold heading molds are widely used in industries requiring high-strength, high-volume fasteners:
Automotive: Bolts, screws, rivets for engine and body assembly.
Construction: Nails, bolts, and structural fasteners.
Electronics: Miniature screws and precision components.
Aerospace: High-performance fasteners with exact tolerances.
Advantages of Using Cold Heading Molds
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Material Efficiency | Minimal waste compared to machining |
| High Precision | Consistent dimensions and quality |
| Enhanced Strength | Work hardening improves mechanical properties |
| Cost-Effective | Suitable for large-scale production |
| Customizable | Can create complex shapes and sizes |
Why Choose a Professional Cold Heading Mold Supplier
Working with a reliable supplier ensures:
Material Quality: High-speed steel, alloy steel, or carbide for durability
Precision Engineering: Tight tolerances for consistent fastener quality
Custom Solutions: OEM/ODM molds for unique fastener designs
After-Sales Support: Maintenance guidance and replacement parts
A cold heading mold is more than just a tool—it is the cornerstone of efficient, high-quality fastener production. By combining precision engineering with durable materials, manufacturers can produce strong, consistent fasteners while reducing waste and costs. For modern industries, investing in high-quality cold heading molds ensures long-term productivity and reliability.