In the world of modern metalworking, cold forging has become one of the most efficient and precise forming processes. It allows manufacturers to produce high-strength, dimensionally accurate parts with minimal waste. At the heart of this process lies the Cold Forging Die, a precision tool that defines the shape, surface quality, and performance of forged components.
This article explores the fundamentals of cold forging, the characteristics of cold forging dies, and why investing in high-quality dies can significantly enhance productivity and part quality.

1. What Is Cold Forging?
Cold forging is a metal forming process performed at or near room temperature, without the need to heat the workpiece beforehand. Unlike hot forging, which requires materials to be heated to extreme temperatures, cold forging relies on high pressure to plastically deform the metal into the desired shape.
This process is especially suitable for ductile metals such as aluminum, copper, and low-carbon steel. It is widely used for producing components that require tight tolerances, excellent surface finish, and enhanced mechanical strength.
Common cold-forged products include:
Bolts, nuts, and screws
Shafts and pins
Automotive parts (gears, housings, fasteners)
Aerospace and precision components
2. What Is a Cold Forging Die?
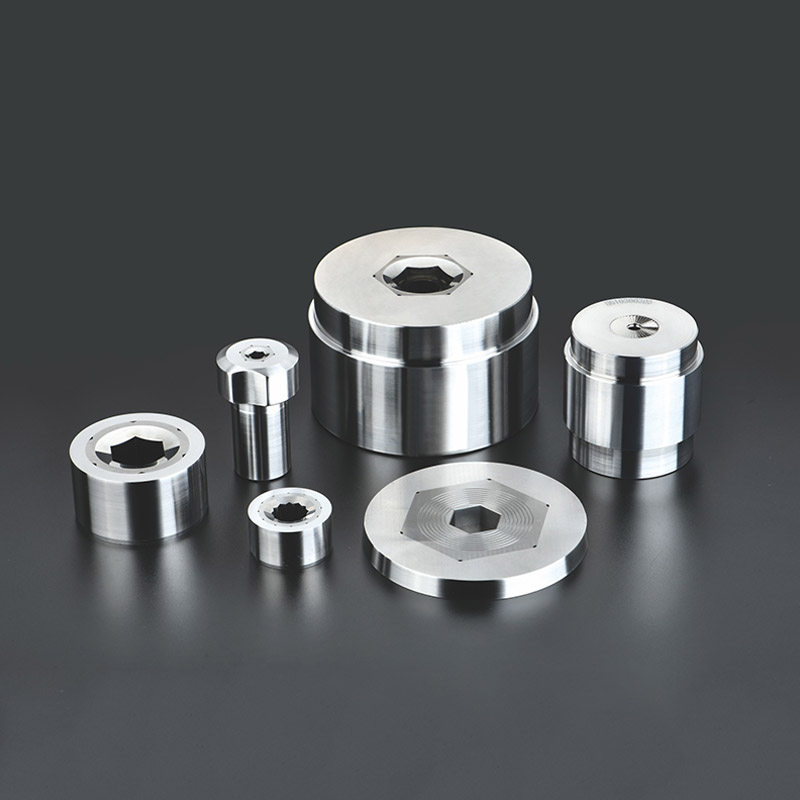
A Cold Forging Die is a specialized tool used to shape metal parts through the cold forging process. It consists of a cavity or series of cavities designed to gradually deform a metal blank under high pressure, ensuring the final shape meets precise dimensional standards.
The die must withstand extreme compressive forces and repeated impact, making tool steel or Tungsten Carbide the preferred materials due to their strength, hardness, and wear resistance.
Cold forging dies generally include:
Upper and lower dies (for forming and shaping)
Punches and sleeves
Insert dies for fine detail and surface finish
Trimming and calibration dies
3. Advantages of Cold Forging
Cold forging offers several advantages over traditional hot forging and machining methods:
High Dimensional Accuracy:
Cold forging produces components with tight tolerances, reducing or eliminating the need for secondary machining.Superior Surface Finish:
Parts come out of the die with smooth surfaces, minimizing polishing or coating steps.Material Efficiency:
Since no material is lost to cutting or melting, cold forging achieves a near-net-shape process with minimal waste.Improved Mechanical Properties:
Work hardening during forging increases the material’s strength, fatigue resistance, and durability.Eco-Friendly Process:
As it requires no heating, energy consumption and carbon emissions are significantly lower.
4. Key Features of Cold Forging Dies
To ensure consistent product quality, cold forging dies must be designed and manufactured with exceptional precision. Below are the most important features:
High Hardness and Strength:
Manufactured from premium-grade Tungsten Carbide or H13 tool steel, ensuring resistance to deformation and wear.Excellent Toughness:
Capable of withstanding repeated impact loads during the forging process.Precision Machining:
Die cavities are CNC machined and polished to achieve micron-level accuracy and superior finish.Heat and Surface Treatments:
Surface nitriding, PVD coating, or carburizing enhances wear resistance and reduces friction.Custom Geometry:
Designed to match specific part dimensions, tolerances, and production volume.
5. Manufacturing Process of Cold Forging Dies
Producing a high-quality cold forging die involves multiple steps of precision engineering and quality control. The general process includes:
Material Selection:
Choosing the appropriate grade of carbide or tool steel based on the forging pressure and material type.CNC Machining:
Advanced multi-axis CNC machines ensure dimensional accuracy and repeatability.Heat Treatment:
Enhances hardness and strength while maintaining toughness.Polishing and Grinding:
Die surfaces are finely ground and polished to achieve the required smoothness.Assembly and Testing:
Each die is carefully assembled, aligned, and tested for performance before delivery.Inspection and Quality Control:
Using CMM, hardness testers, and surface roughness analyzers to ensure quality consistency.
6. Applications of Cold Forging Dies
Cold forging dies are essential in a variety of industrial applications, especially where high strength, durability, and precision are required:
Automotive Industry:
Used to produce engine bolts, drive shafts, gears, and connecting rods.Aerospace and Defense:
Critical components that must meet strict performance and safety standards.Machinery and Tools:
Shafts, bushings, bearings, and other mechanical elements.Electronics and Appliances:
Miniature fasteners and precision hardware parts.Construction and Hardware:
Nuts, bolts, rivets, and other fastening components.
7. Benefits of High-Quality Cold Forging Dies
Choosing a high-quality die can dramatically affect production outcomes. Below are the main benefits manufacturers experience:
Increased Productivity:
Longer die life means fewer replacements and reduced downtime.Cost Efficiency:
Enhanced durability reduces tooling costs and scrap rates.Consistency and Accuracy:
Each part maintains uniform shape, dimensions, and strength.Lower Maintenance Requirements:
Premium materials and coatings minimize wear and reduce the need for frequent adjustments.Smoother Production Flow:
Precision-fit dies ensure stable, high-speed forging operations.
8. Customization and Design Support
Every manufacturing process is unique. That’s why cold forging dies can be fully customized to meet specific needs.
Customization options include:
Die material selection (tungsten carbide, H13, SKD61, etc.)
Die size, shape, and cavity design
Coating (TiN, TiCN, CrN, or DLC)
Forging pressure and stroke compatibility
Special surface treatment for anti-sticking or anti-friction performance
Manufacturers often provide OEM/ODM services, assisting customers from die design and simulation to final production, ensuring optimal forming results.
9. Quality Assurance and Inspection
To maintain superior quality, Cold Forging Die Manufacturers follow strict inspection protocols, including:
Dimensional checks using 3D coordinate measuring systems
Hardness and microstructure testing
Surface finish evaluation
Trial forging tests before shipment
Each die is carefully inspected to ensure it meets industry standards for strength, precision, and durability.
10. Why Choose Our Cold Forging Dies
Our cold forging dies are designed and manufactured using state-of-the-art CNC equipment, advanced heat treatment technology, and premium raw materials.
We offer:
Long die lifespan and exceptional surface quality
Custom die design according to drawings or samples
Competitive factory-direct prices
Short production lead times
Comprehensive technical support and after-sales service
With our expertise in cold forging die manufacturing, we help customers enhance productivity, reduce production costs, and achieve superior quality performance.
11. Maintenance Tips for Longer Die Life
To extend the life of your cold forging dies:
Maintain proper lubrication and cooling during forging.
Clean dies after each production batch to prevent buildup.
Store in a dry, controlled environment.
Inspect regularly for cracks or surface wear.
Regrind or polish periodically to maintain precision.
In a competitive manufacturing environment, the combination of cold forging technology and high-quality cold forging dies is key to achieving efficiency, precision, and strength.
These tools not only determine the accuracy of each forged part but also influence overall production costs and longevity. By investing in durable, precision-engineered cold forging dies, manufacturers can ensure consistent performance and long-term profitability.