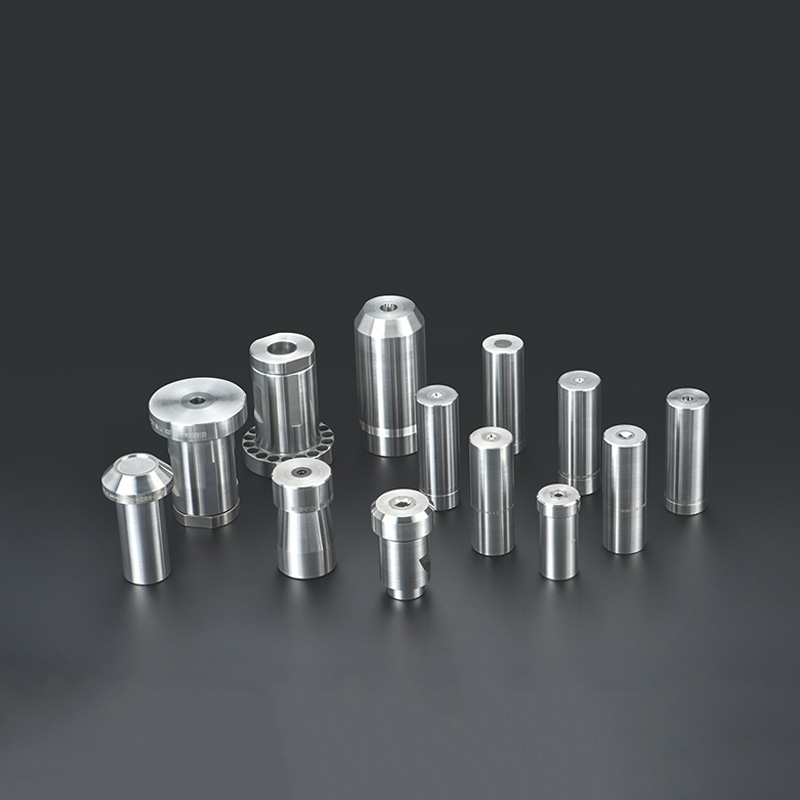
Cold Heading Dies are critical forming tools used in cold heading and cold forging processes to manufacture fasteners such as bolts, screws, nuts, rivets, and special-shaped parts. The performance of a cold heading die directly determines product accuracy, surface quality, production efficiency, and tool life.

Step 1: Understanding Cold Heading Die Functions
A Cold Heading Die works by shaping metal wire into a finished part under high pressure at room temperature. Common types of heading dies include:
Extrusion dies
Trimming dies
Punch dies
In china multi-die cold headers factory production lines, multiple heading die stations work sequentially to form complex fastener geometries.
Step 2: Material Selection for Cold Heading Dies
Tungsten Carbide and Tool Steel
Material selection is the foundation of durable cold heading dies.
Tungsten Carbide Cold Heading Dies offer:
Extremely high hardness
Excellent wear resistance
Long service life in mass production
Carbide cold heading dies are preferred for:
High-speed forming
Stainless steel and alloy steel fasteners
High-volume production environments
For standard applications, high-grade tool steel may still be used, but carbide cold heading die solutions dominate modern fastener manufacturing.
Step 3: Cold Heading Die Design
A well-designed cold heading die ensures dimensional accuracy and tool durability.
Key design considerations:
Material flow path
Die cavity geometry
Stress distribution
Ejection angle
Clearance control
Advanced cold heading tools are often designed to support high-speed cold heading dies for quality parts, reducing forming defects and improving output consistency.
Step 4: Precision Machining of Heading Dies
CNC Machining and EDM
Modern cold heading tooling relies on advanced machining techniques:
CNC turning and milling for outer geometry
Wire EDM and sink EDM for internal cavities
High-precision grinding for die bores
Accurate machining ensures cold heading dies with consistent results across long production runs.
Step 5: Heat Treatment and Sintering
For steel dies:
Vacuum heat treatment improves hardness and toughness
Controlled quenching reduces internal stress
For tungsten carbide cold heading die products:
Powder metallurgy and sintering processes are used
Grain size control is critical for wear resistance
Proper treatment directly supports mould life optimization nut forming dies factory requirements.
Step 6: Surface Finishing and Polishing
Surface quality is essential for product appearance and die longevity.
Mirror polishing reduces friction
Improves metal flow
Enables cold heading dies for smooth surface finish
High-quality polishing also prevents material sticking and galling during forming.
Step 7: Coating and Surface Enhancement
To further improve performance:
TiN, TiCN, or DLC coatings may be applied
Increases wear resistance
Reduces friction
Extends die life
These enhancements are especially important for high-speed cold heading dies for quality parts.
Step 8: Quality Inspection and Testing
Before delivery, cold heading dies undergo strict inspection:
Dimensional measurement
Hardness testing
Surface roughness analysis
Trial production testing
Leading china multi-die cold headers factory suppliers follow international quality standards to ensure reliable tooling performance.
Applications of Cold Heading Dies
High-performance heading dies are widely used in:
Automotive fasteners
Construction bolts and nuts
Electronics screws
Aerospace components
Industrial machinery parts
Advanced carbide cold heading dies are essential for high-strength and precision fastener production.
Choosing the Right Cold Heading Tooling Supplier
When sourcing cold heading tooling, consider:
Experience with tungsten carbide cold heading dies
Ability to customize die design
Proven mould life optimization capability
Stable supply from a reliable nut forming dies factory
Compatibility with multi-die cold heading machines
A trusted supplier ensures productivity and long-term cost efficiency.
Summary: How to Make Cold Heading Dies
To summarize, how to make cold heading dies involves:
Selecting suitable materials such as tungsten carbide
Precision design for optimal metal flow
High-accuracy CNC and EDM machining
Proper heat treatment or sintering
Fine polishing for smooth surface finish
Coating and strict quality control
Well-engineered cold heading dies deliver consistent performance, extended tool life, and superior fastener quality—making them indispensable in modern cold heading operations.